How to create an NFS server

Server-side
Mount new block storage to the server (optional)
If you want to use existing storage in the server. This step can be skipped.
# create new partition:
# NOTE: this will erase existing data in the block storage
parted -s /dev/vdb mklabel gpt
parted -s /dev/vdb unit mib mkpart primary 0% 100%
# Create filesystem:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb1
# Mount the partition
mkdir /mnt/nfs
echo >> /etc/
echo /dev/vdb1 /mnt/nfs ext4 defaults,noatime,nofail 0 0 >> /etc/fstab
mount /mnt/nfsNow the block storage is mounted at /mnt/nfs. Next, we will share this directory as an NFS volume.
Configure a static IP address for private network
If the NFS server is to serve via a public network interface with a static public IP, you can skip this step.
Firstly, attach the private network to the server at your control panel. Suppose the private network has subnet 10.25.96.0/20, the server has MAC address 5a:00:03:e6:4e:78 in this private network.
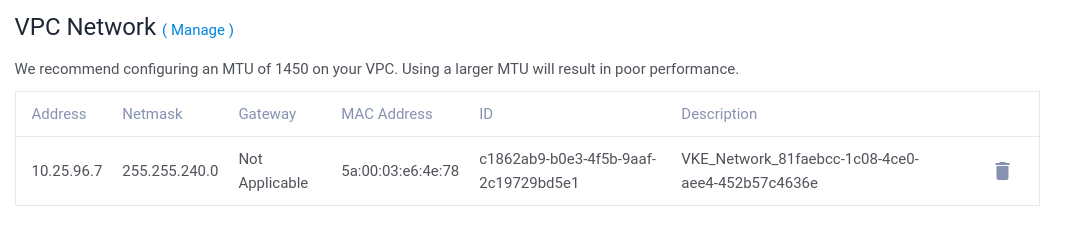
From the screenshot, the server is dynamically assigned with IP 10.25.96.7. We want to assign it another static IP, for instance 10.25.96.100.
Run ip addr to get the network interface enp6s0.
root@nfs-stag:~# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp1s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 56:00:03:e6:4e:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 45.76.111.10/23 metric 100 brd 45.76.111.255 scope global dynamic enp1s0
valid_lft 59605sec preferred_lft 59605sec
inet6 2401:c080:1000:40c5:5400:3ff:fee6:4e78/64 scope global dynamic mngtmpaddr noprefixroute
valid_lft 2591710sec preferred_lft 604510sec
inet6 fe80::5400:3ff:fee6:4e78/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: enp6s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 5a:00:03:e6:4e:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.25.96.7/20 brd 10.25.111.255 scope global enp6s0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::5800:3ff:fee6:4e78/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Create a new netplan config at /etc/netplan/10-enp6s0.yaml. Note: replace enp6s0, macaddresses, addresses appropriately with your information.
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp6s0:
match:
macaddress: 5a:00:03:e6:4e:78
mtu: 1450
dhcp4: no
addresses: [10.25.96.100/20]Run netplan apply to apply the new config. Then, run ip addr to confirm the new configuration.
root@nfs-stag:~# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp1s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 56:00:03:e6:4e:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 45.76.111.10/23 metric 100 brd 45.76.111.255 scope global dynamic enp1s0
valid_lft 86380sec preferred_lft 86380sec
inet6 2401:c080:1000:40c5:5400:3ff:fee6:4e78/64 scope global dynamic mngtmpaddr noprefixroute
valid_lft 2591981sec preferred_lft 604781sec
inet6 fe80::5400:3ff:fee6:4e78/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: enp6s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 5a:00:03:e6:4e:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.25.96.100/20 brd 10.25.111.255 scope global enp6s0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.25.96.7/20 brd 10.25.111.255 scope global secondary enp6s0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::5800:3ff:fee6:4e78/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Setup NFS service
# install NFS server
apt install -y nfs-kernel-server
# start the service
systemctl start nfs-kernel-server
# enable the service in startup
systemctl enable nfs-kernel-server
# update permission on the shared direction
chown nobody:nogroup /mnt/nfs
chmod 777 /mnt/nfsConfigure NFS permission by opening /etc/exports and add the following lines:
# allow access from private network
/mnt/nfs 10.25.96.0/20(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)For an explanation of flags: rw, sync, no_subtree_check, refer to this DO tutorial.
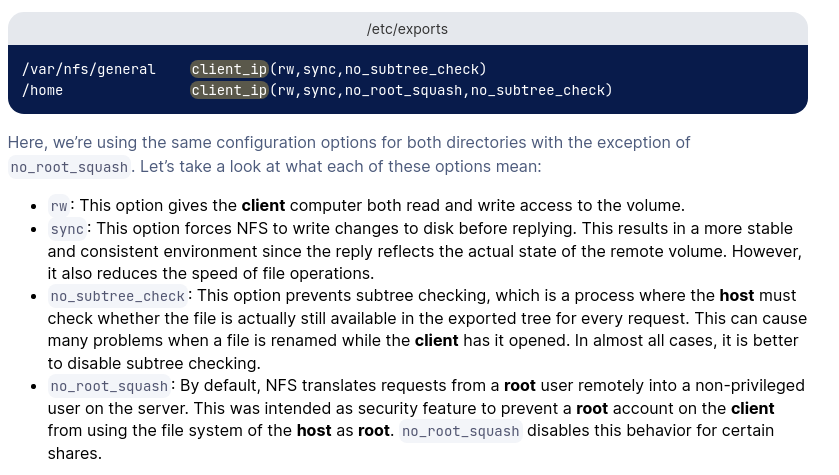
Refresh the NFS server with the new config by exportfs -rva.
Open port for NFS serving
Method 1: with ufw
ufw allow from 10.25.96.0/20 to any port 2049 proto tcpMethod 2: with iptables
Note: iptables changes are not persisted after a restart. You need to create a startup script to run the command. Refer to this post for more info.
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 2049 -j ACCEPT -i enp6s0 -s 10.25.96.0/20enp6s0is the network interface name.-s: is source IP range.-A: append rule.-p: protocol.--dport: port range.-j: jump to the ACCEPT target.
For some old versions, other ports are used.
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 111 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 2049 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 20048 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 111 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 2049 -j ACCEPT
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 20048 -j ACCEPTClient-side
Install the NFS mount util
# Ubuntu
apt install -y nfs-common
# Archlinux
pacman -Syu nfs-utilsOtherwise, you will see the errors:
mount: /opt/nfs: cannot mount 10.25.96.100:/mnt/nfs read-only.# create client directory to mount
mkdir /opt/nfs
# to mount
mount 10.25.96.100:/mnt/nfs /opt/nfs
# to unmount
umount /opt/nfsSome debug commands:
Check port status:
# rpcinfo -p 10.25.96.100
program vers proto port service
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 52554 status
100024 1 tcp 39317 status
100005 1 udp 54399 mountd
100005 1 tcp 53751 mountd
100005 2 udp 33947 mountd
100005 2 tcp 52335 mountd
100005 3 udp 59418 mountd
100005 3 tcp 46289 mountd
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 3 tcp 2049 nfs_acl
100021 1 udp 36258 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 36258 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 36258 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 42535 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 42535 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 42535 nlockmgrCheck port with nmap:
nmap -P -p 2049 10.25.96.100Check the NFS server PID
NFS server is a kernel process and does not stay in the userspace. To list the PID for NFS.
# ps axf
# ps axf | grep nfs
5450 ? I< 0:00 \_ [nfsiod]
6044 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6045 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6046 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6047 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6048 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6049 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6050 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
6051 ? S 0:00 \_ [nfsd]
562 ? Ss 0:00 /usr/sbin/nfsdcld
6919 pts/0 S+ 0:00 \_ grep --color=auto nfs
# cat /proc/fs/nfsd/threads
8
# cat /proc/fs/nfsd/versions # check NFS server version
-2 +3 +4 +4.1 +4.2To debug the mount command use -vvv flag.
NFS in docker container
Refer to these dockers for reference:
https://github.com/sjiveson/nfs-server-alpine
If you are using kubernetes:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nfs-server
labels:
app: nfs-server
spec:
containers:
- name: nfs-server
image: itsthenetwork/nfs-server-alpine:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 2049
name: nfs
# https://github.com/sjiveson/nfs-server-alpine/issues/8#issuecomment-576065566
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs
mountPath: /opt/nfs
securityContext:
privileged: true
capabilities:
add:
- NET_ADMIN
- SETPCAP
restartPolicy: Always
volumes:
- name: nfs
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nfs-server
spec:
ports:
- port: 2049
selector:
app: nfs-server

